Introduction
Everyday, developers stare at a web of prompts, retrievers, and evaluators trying to guess why an agent failed. Pipelines call half a dozen models, tools trigger other tools, yet no one can see what actually happens within each step from input to chain to output
Developers still think the “fix” is better prompts or new frameworks.
LangChain today, CrewAI tomorrow, or adding new agents, but the core problem isn’t in orchestration, it’s in observability. You can’t improve what you can’t observe.
Understanding an agent means tracing every step of its reasoning: how it interpreted a user query, what context it fetched, which tools it called, how long it spent thinking, and what it cost. Which is exactly what FutureAGI’s TraceAI makes visible.
Instead of adding another abstraction layer, it exposes what your stack is already doing, every LLM call, every retriever hit, every tool invocation as standardized, OpenTelemetry-compatible spans.
With TraceAI, debugging stops being a post-mortem. You see your agent’s reasoning trail unfold in real time complete with context, cost, and sequence so you can actually fix what matters, not just guess.
Why Instrumentation Matters
AI agentic systems aren’t static. They evolve, adapt, and depend on multiple moving parts: models, retrievers, prompts, memory storage, orchestration, and external tools.
Without tracing:
You can’t debug failures - Why did the agent pick the wrong answer?
You can’t measure latency or token usage across steps.
You can’t visualize the workflow across multiple frameworks (LangChain, CrewAI, DSPy, etc.)
Traditional logs tell you what happened.
Tracing tells you how it happened.
TraceAI standardizes this process so that every prompt, embedding, retrieval, and response is automatically captured, versioned, and observable.
What Is TraceAI?
TraceAI is an open-source (OSS) package that enables standardized tracing of AI applications and frameworks.
It extends OpenTelemetry, bridging the gap between infrastructure-level traces (API calls, latency, errors) and AI-specific signals like:
Prompts and responses
Model name and parameters
Token usage and latency
Tool invocations
Guardrail or evaluator outcomes
TraceAI works out-of-the-box with multiple orchestration frameworks like Langchain, CrewAI, OpenAI et and can export to any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend or directly into Future AGI’s observability platform.
Features at a Glance
✅ Standardized Tracing: Maps AI workflows to consistent trace attributes and spans.
✅ Framework-Agnostic: Works with OpenAI, LangChain, Anthropic, CrewAI, DSPy, and many others.
✅ Extensible Plugins: Easily add instrumentation for unsupported frameworks.
✅ Future AGI Native Support: Optimized for full-stack observability with trace-to-eval linkage.
Supported Frameworks
Framework | Package | Description |
OpenAI | traceAI-openai | Traces OpenAI completions, chat, image, and audio APIs |
LangChain | traceAI-langchain | Instruments chains, tools, retrievers |
CrewAI | traceAI-crewai | Observes agentic multi-actor pipelines |
DSPy | traceAI-dspy | Traces declarative program steps |
Anthropic, Mistral, VertexAI, Groq, Haystack, Bedrock, etc. | — | Full cross-vendor support |
(All available on PyPI under traceAI-* packages.)
Quickstart: Your First Trace
Step 1 - Install the Package
Step 2 - Set Environment Variables
Step 3 - Register the Tracer Provider
This connects your app to Future AGI’s observability pipeline (or any OTEL backend):
Step 4 - Instrument Your Framework
Now, every OpenAI call automatically emits spans with attributes like model name, latency, prompt length, and cost.
Step 5 - Interact with your framework
You’ve just created your first observable AI.
Each run will appear as a trace with spans representing prompt input, LLM execution, and response generation.
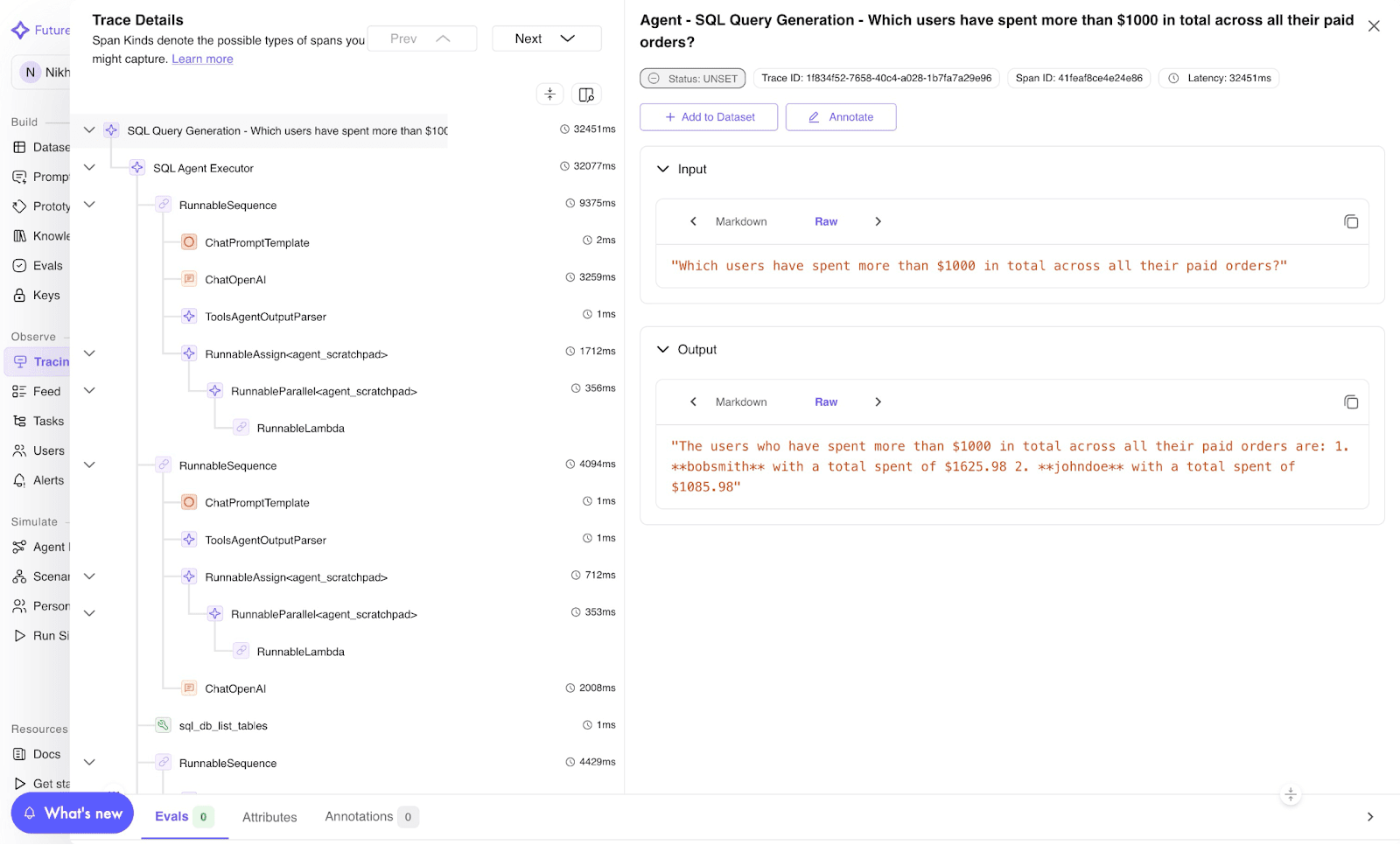
Image 1: TraceAI Trace Visualization Dashboard
Manual Instrumentation with TraceAI Helpers
While framework-level auto-instrumentation works for most cases, sometimes you want fine-grained control over what gets traced.
That’s where traceAI Helpers come in. These are lightweight decorators and context managers that let you manually trace functions, chains, and tools.
7.1 Setup
7.2 Function Decoration
✅ Captures input/output automatically
✅ Auto-assigns span status
✅ Ideal for wrapping full functions or chain steps
7.3 Code Block Tracing
✅ Perfect for tracing specific blocks
✅ Lets you set attributes manually (e.g., tool parameters, results)
7.4 Span Kinds
TraceAI defines semantic span kinds for different components:
Span Kind | Use Case |
CHAIN | General logic or function |
LLM | Model calls |
TOOL | Tool usage |
RETRIEVER | Document retrieval |
EMBEDDING | Embedding generation |
AGENT | Agent invocation |
RERANKER | Context reranking |
GUARDRAIL | Compliance checks |
EVALUATOR | Eval span |
These kinds make your traces semantically rich and visually distinct in dashboards.
7.5 Example: Agent Span
7.6 Example: Tool Span
Every decorator automatically generates spans that include:
Input and output data
Tool metadata
Execution status
All visible in your Future AGI trace view.
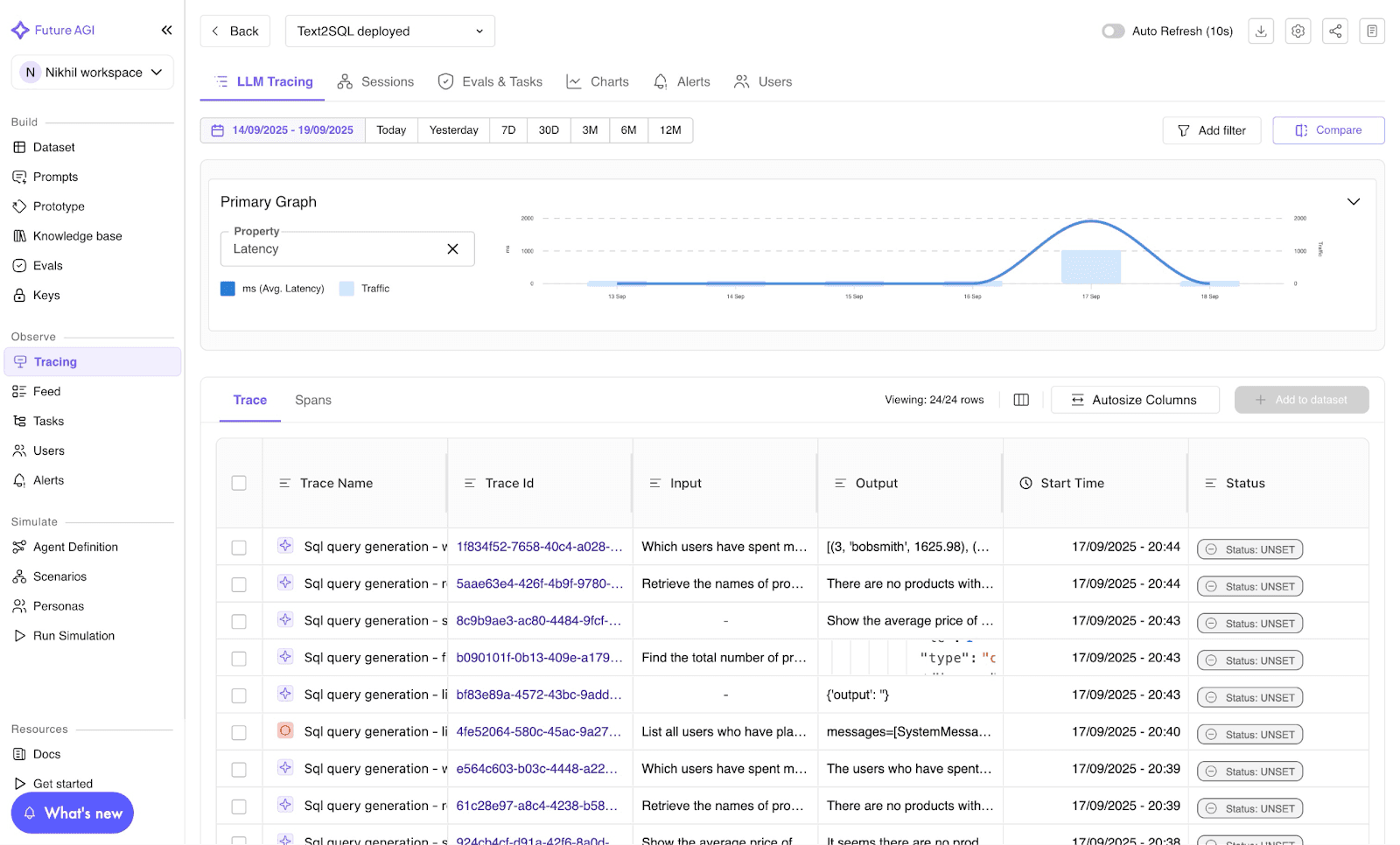
Image 2: Future AGI LLM Tracing Dashboard
Visualizing Traces
Connect TraceAI to Future AGI’s own Observe to visualize spans as nested timelines.
Each node represents a span:
LLM call → model name, latency, tokens
Tool execution → input/output details
Agent span → full decision context
This makes debugging, optimization, and auditability effortless.
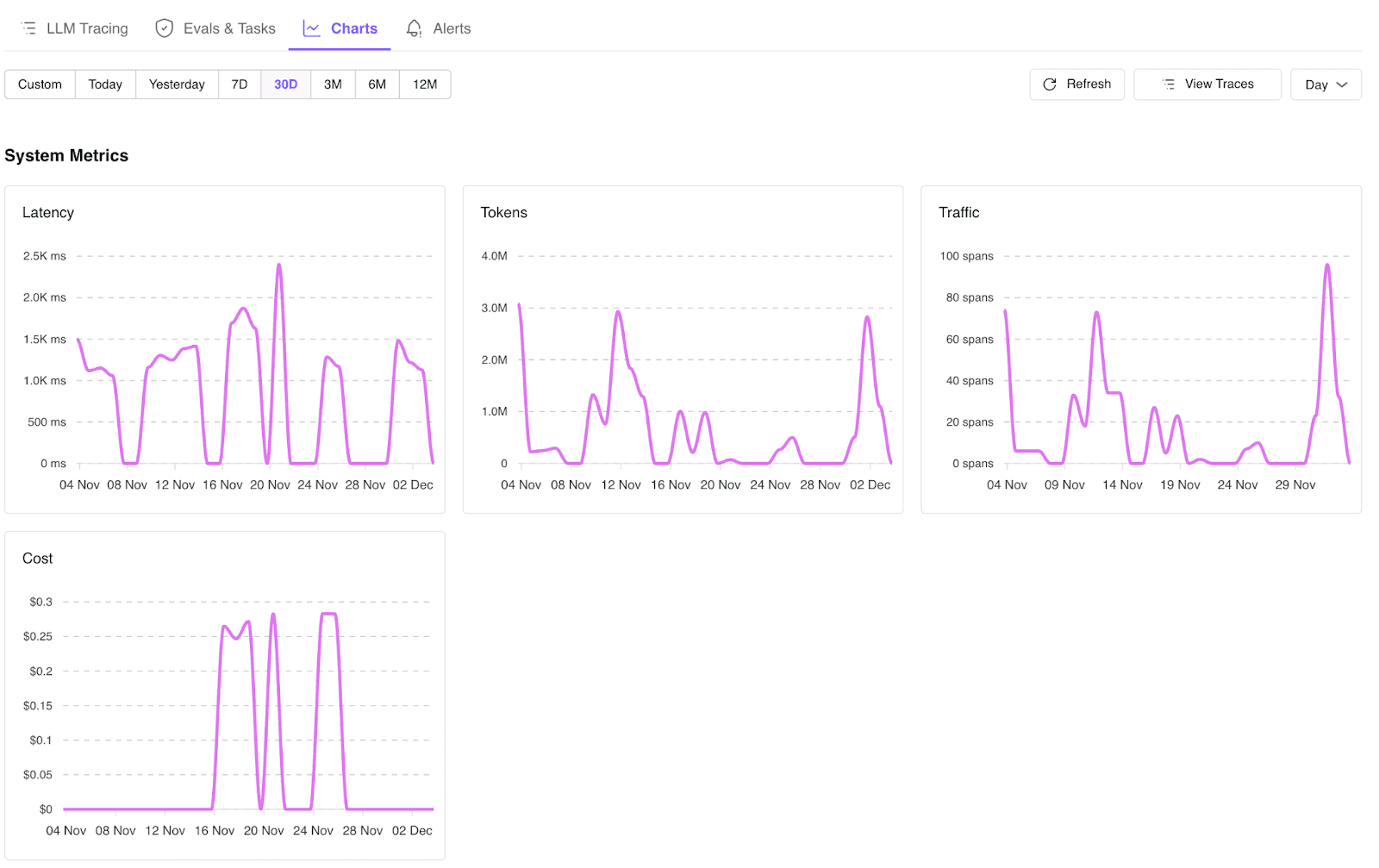
Image 3: TraceAI System Metrics Dashboard
Best Practices
✅ Use decorators for simplicity; context managers for precision.
✅ Name spans meaningfully (fi_span_kind="agent", name="retriever-step").
✅ Combine with Future AGI Evaluate to correlate trace performance with eval metrics.
✅ Use environment-based project versions to separate dev/staging/prod.
✅ Add TraceAI early as retro-instrumentation is harder later.
Troubleshooting
Missing spans? Verify your
trace_providerregistration.OTEL backend not visible? Ensure your collector endpoint is running.
Sensitive data exposure? Use redaction utilities before setting inputs/outputs.
Contribution
TraceAI is open-source and community-driven.
To contribute:
git clone https://github.com/future-agi/traceAI |
Then submit a PR!
Join the Future AGI community on LinkedIn, Twitter, or Reddit.
Observability is no longer a hurdle.
The best AI systems don’t just generate answers, they explain how they got there.
TraceAI makes that explanation visible, measurable, and improvable.
Ready to see your agents come alive with full trace visibility?
👉 Get started now: github.com/future-agi/traceAI
FAQs
What is traceAI in simple terms?
How is traceAI different from traditional APM or logging tools for AI?
Which AI frameworks and LLM providers does traceAI support today?
How does traceAI use OpenTelemetry for AI observability?