Introduction
Voice AI agents handle thousands of conversations per day, but most production systems only discover failures after customers have already hung up frustrated. Traditional APM tools track response times and error rates, but they miss what actually breaks in voice AI: conversation quality. Your infrastructure metrics might look perfect while customers abandon calls because your agent misclassifies intents or loses dialog state.
Voice AI operates differently than standard web applications. You're dealing with multi-turn conversations that maintain context across exchanges, real-time audio streams that introduce latency and quality variables, and LLM inference chains that behave probabilistically rather than deterministically. Traditional monitoring tools can't detect when your model starts drifting or when semantic accuracy drops below acceptable thresholds.
Performance drift sneaks in as your agent encounters new accents, background noise patterns, or edge cases that weren't in your training data. By the time customer complaints surface, you've already lost trust and revenue. Standard APM solutions report that services are healthy while users experience frustration that never triggers an alert.
In 2026, voice AI systems will handle millions of conversations daily across customer service, sales, and support channels. You need observability that tracks conversation success rates, semantic accuracy, turn efficiency, and sentiment in real time, not just infrastructure uptime.
In this blog, we'll walk through how to implement voice AI observability for real-time production monitoring that catches issues before your customers do.
Core Metrics Every Voice AI Team Should Track
Voice AI monitoring isn't about tracking one "golden signal" but correlating performance across four critical dimensions.
2.1 Latency Metrics
Time-to-First-Byte (TTFB): Measure the delay between user silence and the first audio packet returned by your agent to keep conversational flow natural.
End-to-End Turn Latency: Track the total time from user input to agent response completion, including transcription, LLM inference, and TTS generation.
TTS Processing Lag: Monitor the delta between text generation and audio rendering to catch bottlenecks in your synthesis pipeline.
2.2 Quality Metrics
Word Error Rate (WER): Calculate transcription accuracy by comparing ASR output against ground-truth logs to identify domain-specific vocabulary failures.
Intent Classification Confidence: Track the model's confidence scores for intent recognition to spot vague user queries or training data gaps.
Task Success Rate: Measure the percentage of conversations where the user's primary goal (e.g., booking an appointment) was fully completed without human intervention.
Business Metrics
Average Handle Time (AHT): Monitor session duration to ensure agents resolve issues efficiently rather than trapping users in endless loops.
First Contact Resolution (FCR): Track how often users' issues are solved in a single session without needing a callback or second attempt.
Escalation Rate: Measure the frequency of handoffs to human agents, differentiating between planned handoffs and failure-driven escalations.
2.3 Audio Metrics
Mean Opinion Score (MOS): Use automated algorithms to estimate audio clarity and quality on a scale of 1-5, flagging calls that sound robotic or distorted.
Jitter and Packet Loss: Monitor network stability metrics that cause choppy audio or robotic voice artifacts during real-time streaming.
Barge-in Failure Rate: Track instances where the agent failed to stop speaking when the user interrupted, a key driver of poor user experience.
2.4 Setting Alert Thresholds That Actually Matter
Your dashboard is useless if it lights up red for every minor fluctuation. You need actionable alerts that distinguish between noise and actual degradation.
2.4.1 P95 Latency vs. Average Latency Alerts
Average latency hides the frustration of your "tail" users. If 5% of your calls have 3-second delays, that's hundreds of angry customers a day, even if your average looks fine.
Alert Type | What It Tracks | Why It Matters for Voice AI |
Average Latency | The mean response time across all calls. | Good for long-term trending but masks intermittent spikes that ruin user trust |
P95 / P99 Latency | The experience of your slowest 5% or 1% of users. | Critical for detecting specific edge cases, regional outages, or complex queries causing timeouts |
Spike Duration | How long latency stays elevated above a threshold. | Differentiates a momentary network outage from a sustained infrastructure failure |
2.4.2 Anomaly Detection vs. Static Thresholds
Static thresholds work for hard limits (like server down), but they fail for metrics that naturally fluctuate with traffic patterns
Feature | Static Thresholds | Anomaly Detection (Dynamic) |
Definition | Hard limits (e.g., "Alert if latency > 800ms"). | Adaptive baselines based on historical patterns |
Best For | SLAs, hard infrastructure limits, and binary up/down checks. | Detecting subtle performance drift, seasonal traffic spikes, and "unknown unknowns" |
Maintenance | High: requires manual tuning as your system scales or changes. | Low: automatically adjusts to new normal patterns over time |
2.5 Alert Fatigue: How to Avoid Noise While Catching Real Issues
Alert fatigue destroys on-call sanity. Instead of alerting on every raw metric spike, group related alerts into "incidents" and route them based on severity page engineers only for sustained P95 degradation or widespread error spikes, while logging transient jitter warnings for later review.
Future AGI tracks your voice agents in production with real-time insights across all these metrics, automatically pinpointing root causes when latency spikes or quality drops below your thresholds. The platform evaluates audio, detects anomalies across conversation flows, and gives you actionable feedback without requiring you to build custom monitoring infrastructure from scratch.
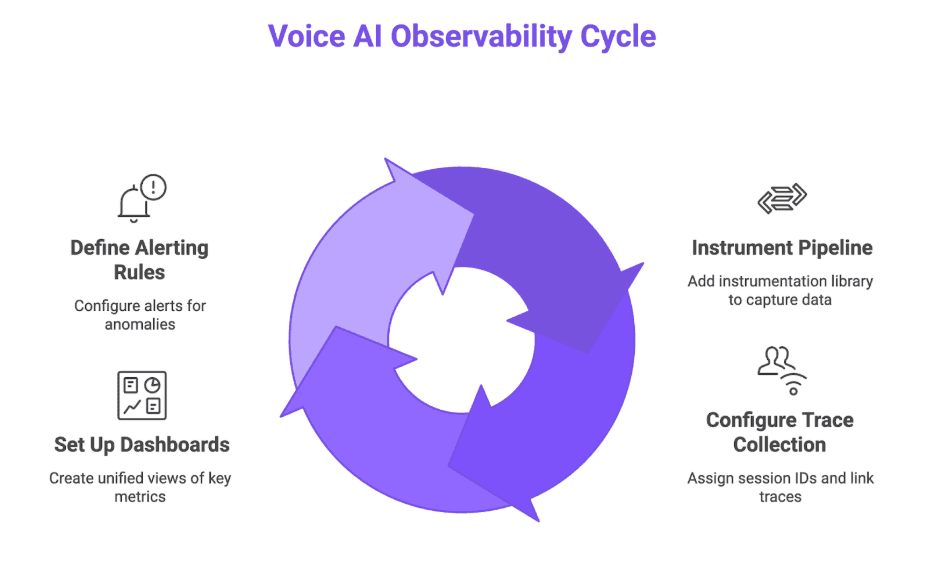
Figure 1: Voice AI Observability Cycle
Setting Up Voice AI Observability With Future AGI
Step 1: Instrument Your Voice Pipeline
Add Future AGI's instrumentation library to your voice pipeline with a few lines of code that wrap your existing OpenAI, Anthropic, or custom LLM calls. The SDK automatically captures audio input, transcription output, LLM reasoning steps, and TTS generation without requiring you to manually log each component.
Step 2: Configure Trace Collection for Conversation Flows
It assigns a unique session ID to each conversation and links all traces (user turns, agent responses, tool calls) under that session for complete multi-turn visibility. You define what constitutes a "session" based on your use case, whether it's a single phone call, a 24-hour window, or until the user explicitly ends the conversation.
Step 3: Set Up Dashboards for Key Metrics
It provides pre-built dashboards that surface latency percentiles, audio quality scores, task completion rates, and business metrics like escalation frequency in one unified view. You can customize these dashboards to focus on the metrics that matter most for your team, filtering by time range, user segment, or specific conversation types.
Step 4: Define Alerting Rules and Anomaly Detection
Configure alerts based on P95 latency thresholds, sudden drops in task success rate, or spikes in audio quality degradation using Future AGI's built-in anomaly detection. The platform learns your normal traffic patterns and automatically adjusts baselines, so you only get paged when something genuinely breaks rather than for every minor fluctuation.
Integration Time: Hours, Not Weeks
Future AGI integrates with your existing workflow in hours because it supports standard OpenTelemetry instrumentation and provides native SDKs for popular frameworks. You keep your current voice pipeline architecture and simply add observability on top, without rewriting code or migrating infrastructure.
Tracing Conversations: From First Word to Resolution
4.1 End-to-End Conversation Tracing
Session-level visibility: Every conversation gets a unique session ID that links all user turns, agent responses, tool calls, and audio events under one trace, so you can replay the entire interaction from start to finish.
Component-level breakdown: Each trace breaks down latency by component (STT processing time, LLM inference duration, TTS generation lag) to pinpoint exactly where delays accumulate in your pipeline.
4.2 Linking Audio Events to LLM Calls to Tool Executions
Causality chains: When your agent makes a tool call to check inventory or book an appointment, the trace connects that action back to the specific audio input that triggered it, preserving the full context chain.
Failure Chains: When your audio stream has network issues like jitter or packet loss, your STT service mishears what the user said. Those transcription mistakes mean your LLM gets the wrong text, classifies the intent incorrectly, and calls the wrong tool or API.
4.3 Debugging Specific Conversation Failures
Search and replay: When a user reports a bad interaction, search for their conversation by session ID or timestamp, inspect the full trace, and see exactly where your agent misunderstood input or generated an inappropriate response.
Confidence score tracking: You need to configure evaluations on your traces to capture confidence scores at each step, like transcription accuracy, intent classification certainty, and TTS quality estimates. Set thresholds for each component so you can filter conversations where low confidence led to failures.
Future AGI automatically captures every step in your voice agent's execution, from audio input through STT, LLM reasoning, tool calls, and TTS output, all linked under a single conversation trace. When production issues arise, you can drill into individual spans to identify whether the failure originated in speech recognition, intent classification, or downstream API calls, accelerating debugging and iteration.
Anomaly Detection: Catching Drift Before Customers Do
5.1 What Causes Performance Drift?
Performance drift creeps in when your training data stops reflecting production reality, whether from model version updates that change inference behavior, shifts in customer language patterns (new slang, regional accents, industry jargon), or infrastructure changes like switching STT providers or adjusting load balancing rules. Voice AI agents encounter seasonal variations, evolving user behaviors, and edge cases that weren't represented in initial training sets, causing gradual accuracy degradation that compounds over weeks or months.
5.2 Automated Anomaly Detection vs. Manual Monitoring
Aspect | Manual Monitoring | Manual Monitoring |
Detection Speed | Hours to days after issues surface through customer complaints or periodic reviews | Real-time alerts within minutes when metrics deviate from learned baselines |
Coverage | Limited to metrics you explicitly check, missing subtle drift in unchecked dimensions | Continuous monitoring across all tracked metrics, catching drift in unexpected areas |
Scalability | Doesn't scale beyond a few key metrics due to human review bottlenecks | Automatically scales to monitor hundreds of conversation flows and thousands of sessions daily |
False Positive Rate | Low because humans validate before escalating, but slow response time | Can be noisy without proper threshold tuning, but catches issues before customer impact |
Root Cause Analysis | Deep manual investigation reveals "why" but requires significant time investment | Quickly identifies "what" and "when" with correlation analysis, reducing MTTD (Mean Time to Detect) |
5.3 Real Example: Catching a 4% Accuracy Drift
A voice agent handling insurance claims started showing a 4% drop in intent classification accuracy over two weeks, triggered by customers adopting new terminology like "virtual inspection" instead of "photo claim" after a marketing campaign. Manual monitoring would have missed this gradual decline, but automated anomaly detection flagged the confidence score drop and escalated before the accuracy dip caused noticeable business impact.
When Future AGI detects drift, it correlates the anomaly across multiple dimensions (latency, accuracy, confidence scores, user demographics) to pinpoint root causes rather than just surfacing a generic "something broke" alert. You get actionable feedback showing which specific conversation types or user inputs trigger failures, so you can retrain models with targeted data, adjust prompts, or roll back recent changes before the drift compounds.
Building Observability Into Your Voice AI Workflow
6.1 Connecting Observability to Pre-Production Testing
Observability shouldn't start when you deploy to production. Future AGI's Simulate runs thousands of synthetic test conversations against your voice agent before launch, evaluating actual audio output for latency spikes, tone inconsistencies, and quality degradation that transcripts completely miss. You catch the 800ms latency spike or robotic tone shift during testing instead of discovering it through customer complaints.
6.2 Using Production Data to Improve Test Scenarios
The best test scenarios come from real failures your agent encounters in production. Future AGI captures production traces showing where conversations break down, then feeds those edge cases back into your pre-production test suite so you can validate fixes against actual user behavior patterns. Synthetic test generation works for coverage, but production logs reveal the specific accent variations, background noise patterns, and unexpected phrasings that cause real failures.
6.3 The Continuous Improvement Loop: Observe → Evaluate → Optimize
Observe: Monitor production traffic in real time to identify patterns in failed conversations, low confidence scores, high latency outliers, or drops in task completion rates. Set aside time weekly to review traces and spot recurring failure modes rather than waiting for escalations.
Evaluate: Run targeted experiments comparing different prompts, model versions, or pipeline configurations against production-like scenarios to quantify improvement. Use golden datasets derived from real user interactions to ensure your changes actually solve customer-facing problems.
Optimize: Deploy changes incrementally, track metrics before and after, and validate that the fix improved target KPIs without regressing other dimensions. Feed evaluation results back into your training data and observability baselines to create a self-improving system.
6.4 Team Workflows: Who Sees What, When
Engineers get real-time alerts for P95 latency spikes and error rate increases, product managers see dashboards tracking task success rates and escalation frequency, and ML teams review weekly reports on confidence score distributions and drift patterns. Future AGI routes alerts based on severity and context, so on-call engineers only get paged for sustained degradation while lower-priority observations get logged for batch review during sprint planning.
Conclusion
Reliable voice AI needs more than just uptime monitoring; it requires deep observability into conversation quality, audio streams, and user intent. By tracking P95 latency, transcribing actual production calls, and setting automated alerts for performance drift, you catch issues before they impact your customers. Future AGI gives you this visibility out of the box with SDKs that drop into your existing Python or Node.js workflows. Don't wait for a support ticket to tell you something's broken.
Start monitoring your voice AI in production with free tier. Sign up for Future AGI and instrument your first voice pipeline in under an hour.
FAQs