Introduction
Voice AI agents that make calls or collect personal data carry serious legal risks if not managed correctly. In 2025, a healthcare provider's voice AI system failed its HIPAA audit and faced a $2.3 million fine because the AI logged patient conversations for 90 days instead of the required 30-day deletion window. The system was shut down for three weeks.
The FCC’s February 8, 2024 Declaratory Ruling treats AI-generated voices as artificial under the TCPA, which means your agent needs documented prior express written consent before making calls to mobile phones or residential lines. Industry rules stack on top of telecom law. In healthcare, audio recordings that can identify a person and relate to care or payment qualify as PHI, which makes storage, access control, and audit logs legally required.
Here is the actual problem: running manual compliance checks across consent flows, disclosure timing, PII handling, and data retention policies does not scale when your agent handles hundreds of calls per day. You need automated testing that simulates edge cases, real-time monitoring that flags violations as they happen, and audit trails that prove compliance to regulators without reconstructing logs by hand.
This post walks through how to audit voice AI agents before launch, where compliance breaks happen most often, and how to automate testing and monitoring so you catch issues in staging instead of production.
Why Voice AI Audits Are More Complex Than You Think
Most teams underestimate how hard it is to audit a voice AI system properly. Unlike static software, voice agents operate in real time across multiple failure modes that only surface under production load. A compliance violation might appear once in 100 calls. A rare text-to-speech glitch might only happen when a specific word is used. If you're testing randomly or treating all calls the same, you're missing the high-impact problems.
Manual auditing doesn't scale. QA teams fall back on small sample audits or "happy path" testing, which leaves large sections of potential failure modes unchecked. Financial institutions face an even harder compliance bar. They must obtain consent before proceeding, or face penalties. JP Morgan was fined $200 million by the CTFC in 2024 after billions of order messages, including phone calls, were missed from data capture due to a system operating error.
Here's what makes voice AI audits uniquely difficult:
Scale problem: You need to test thousands of conversation paths, not just 10-20 happy scenarios.
Timing issues: Disclosures must happen at specific conversational moments, not just "somewhere in the call".
Multi-component systems: Your agent touches ASR, LLM, TTS, CRM, and analytics tools, each with its own failure mode.
Real-time constraints: You can't pause production calls to check if PII was logged correctly.
Regulatory complexity: TCPA, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR, and state laws all apply differently based on what your agent does.
Most teams realize they need professional audit infrastructure only after their first close call with a regulator or after discovering PII in logs that shouldn't be there.
The PII Leak Problem No One Talks About
PII leaks are not edge cases. They are production realities that happen more often than teams admit. A global bank used monitoring tools to track internal AI across 80,000 employees and within 60 days identified dozens of behavioral patterns, including seasonal PII spikes, that enabled targeted intervention before systemic exposure occurred.
Here's how PII leaks happen in voice AI systems:
Observability blind spot: Your logging platform captures full request/response payloads. Customer emails, phone numbers, and account IDs sit in logs accessible to your entire engineering team, retained for 30-90 days. A healthcare AI startup logged doctor-patient conversations for debugging and had 60 days of HIPAA violations sitting in CloudWatch before they realized it.
Third-party integrations: Your LLM provider might store prompts or completions for training. Your analytics tool might capture unredacted transcripts. Your CRM sync might log raw audio files.
Training data pipelines: Teams store interaction data for model improvement without proper redaction. PII flows into training datasets, embeddings, and vector stores.
Weak access controls: Logs often have weaker access controls than your database. They get shipped into third-party monitoring tools. Every extra copy is an opportunity for a breach.
Voice AI Compliance Audit Framework
A voice AI compliance audit checks whether your agent meets legal, security, and disclosure rules before you ship to production. Think of it as a structured pre-flight checklist that covers data flows, consent mechanisms, and access controls in one pass.
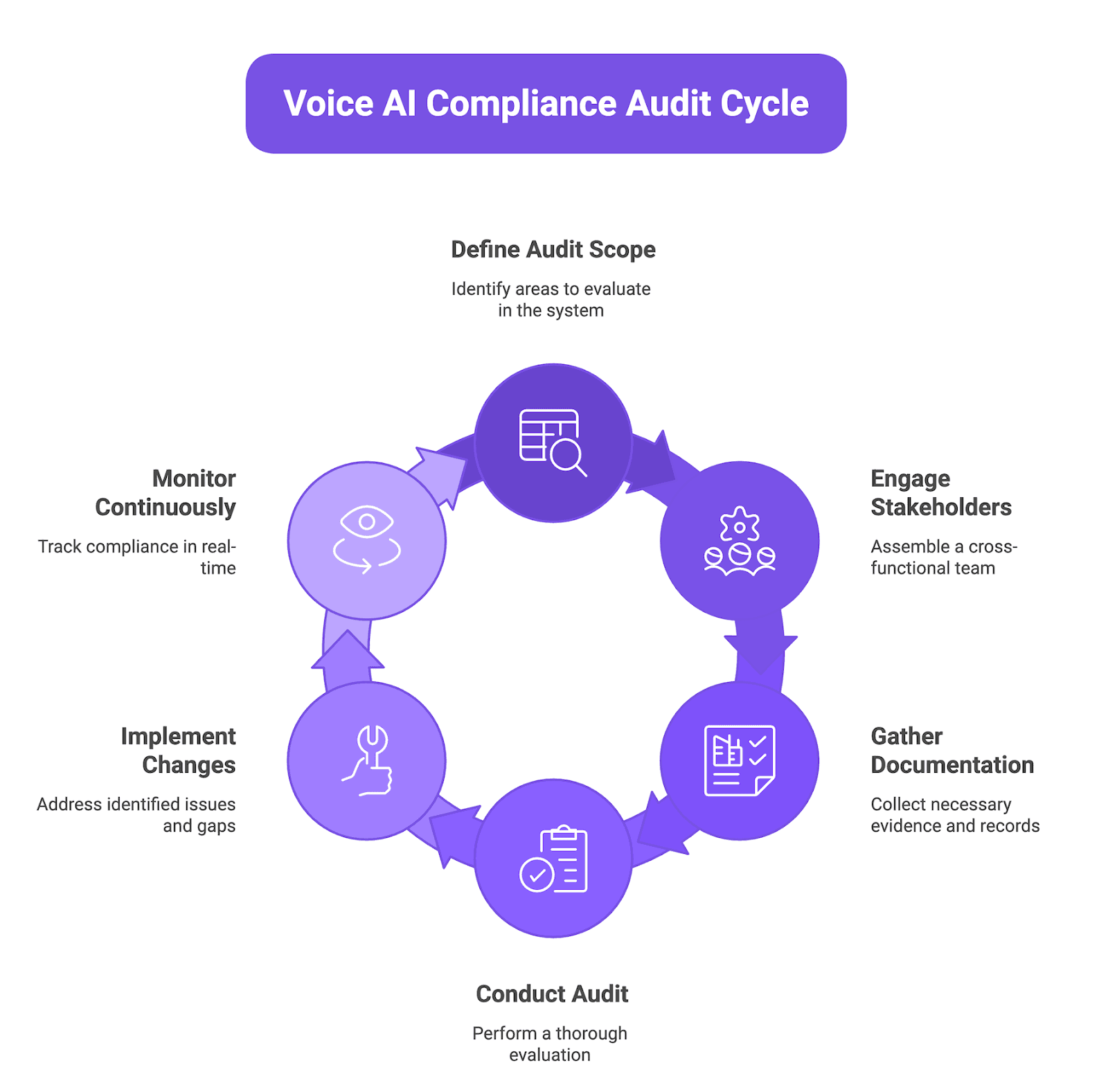
Figure 1: Voice AI Compliance Audit Cycle
4.1 Audit scope: What to evaluate in a voice AI system
Your audit needs to cover every point where voice data enters, moves, or exits the system. Start with the components that touch user input and work backward through processing, storage, and integrations.
Call initiation logic (outbound dialing, consent checks, opt-out handling)
Audio capture and real-time transcription pipelines
Data storage (recordings, transcripts, metadata, logs)
Third-party integrations (LLM providers, CRM systems, analytics tools)
User-facing features (recording disclosures, AI identification, opt-out flows)
4.2 Stakeholders: Legal, security, engineering, operations
Run the audit as a cross-functional team so you catch issues early instead of after launch. Each group brings a different lens: legal spots consent gaps, security finds access control holes, engineering validates implementation, and operations confirms monitoring is working.
Legal reviews consent flows, disclosure scripts, and data retention policies
Security audits encryption, access logs, and authentication mechanisms
Engineering verifies code, API configs, and error handling
Operations tests monitoring dashboards, alert triggers, and incident response
4.3 Documentation requirements: What auditors need to see
Auditors expect evidence, not promises, so keep logs and policy docs current and accessible. You need proof that controls are live and that you can trace data from collection to deletion.
System architecture diagrams showing data flows and processing boundaries
Consent collection records with timestamps and IP addresses
Encryption certificates and key management procedures
Access control policies with role definitions and review dates
Incident response plans with test dates and results
4.4 Audit frequency: Pre-launch, periodic, and continuous
Run a full audit before your first production call, then schedule quarterly reviews or after major feature releases. Add real-time monitoring so you catch policy violations as they happen instead of weeks later.
Pre-launch: full audit covering all framework areas before go-live
Quarterly: scheduled reviews of controls, logs, and policy updates
Post-change: audit after new integrations, model updates, or feature launches
Continuous: automated monitoring for consent failures, unauthorized access, and data retention violations
The Three Pillars of Voice AI Compliance
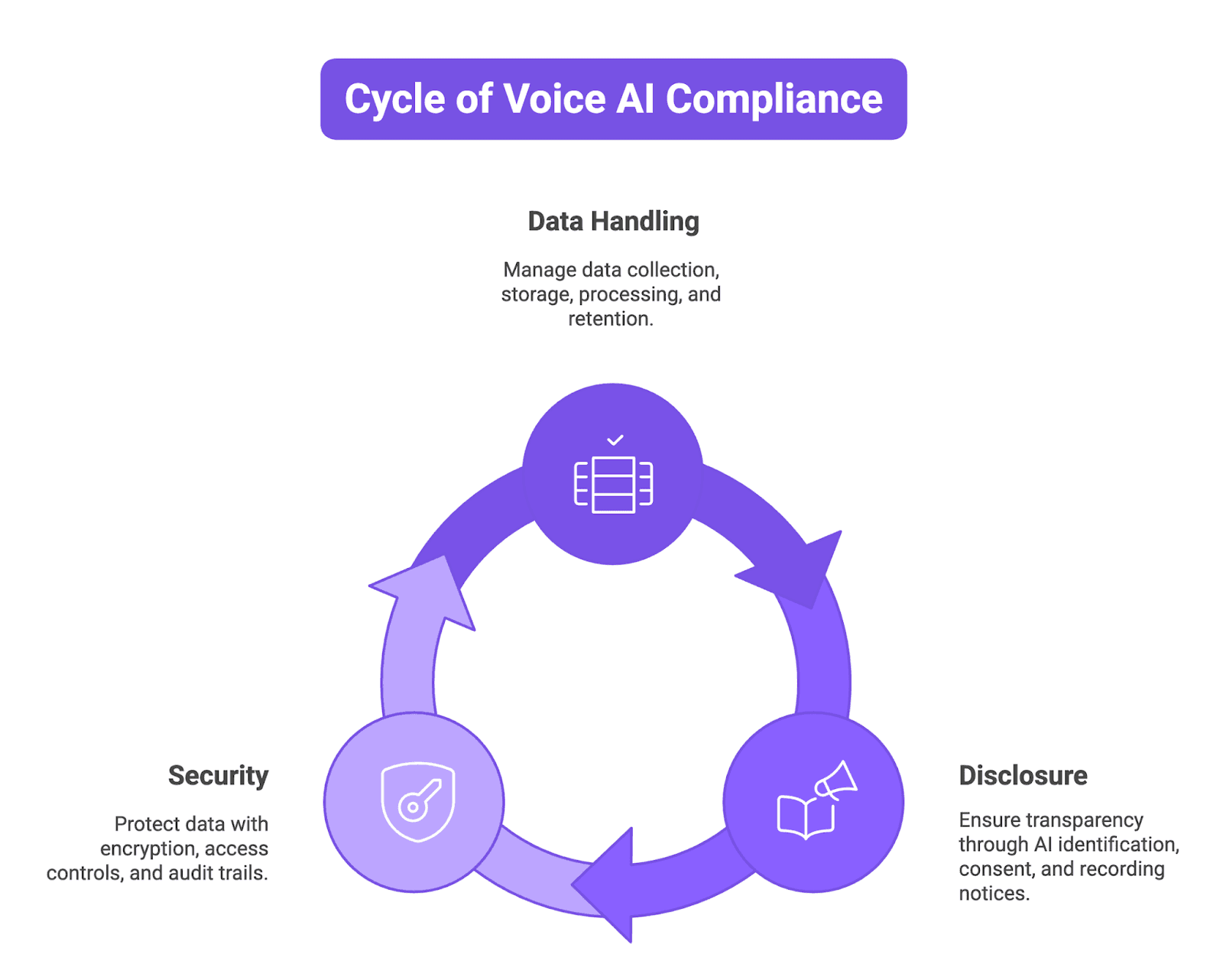
Figure 2: Three Pillars of Voice AI Compliance
5.1 Data handling: Collection, storage, processing, retention
Your data handling practices determine whether you can prove compliance under HIPAA, GDPR, or state privacy laws.
Collection: capture only the data you need, log consent at the point of collection, and flag sensitive categories like PII(Personally Identifiable Information), payment info, biometrics).
Storage: encrypt recordings and transcripts at rest using AES-256, isolate environments by customer or workload, and use a KMS or HSM for key management.
Processing: apply role-based access controls so only authorized services can read voice data, use secure APIs for third-party integrations, and log every access event.
Retention: delete recordings after the policy window expires, automate purge workflows, test deletion procedures quarterly, and keep immutable audit logs of deletion events.
5.2 Disclosure: AI identification, consent, recording notices
Transparency requirements now apply across telecom, privacy, and emerging AI-specific regulations.
AI identification: Disclose that the caller is speaking with an AI agent at the start of the conversation, use clear language (avoid "virtual assistant" or vague terms), and log the timestamp of disclosure.
Consent: obtain express written consent for TCPA-covered calls, store consent records with date, method, and IP address, and provide an easy opt-out mechanism.
Recording notices: announce call recording before sensitive data is collected, respect state two-party consent laws, and include opt-out instructions in the notice.
5.3 Security: Encryption, access controls, audit trails
Security controls protect voice data from unauthorized access and provide the audit trail you need for compliance reviews.
Encryption: use TLS/SRTP for voice streams in transit, apply AES-256 encryption for stored recordings, and manage keys through a centralized KMS with rotation policies.
Access controls: implement role-based access control (RBAC) with least privilege, require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for admin consoles and APIs, and review permissions quarterly.
Audit trails: log every access to voice data with user ID, timestamp, and action type, store logs in immutable storage for compliance retention periods, and set up alerts for unusual access patterns.
Pre-Launch Compliance Checklist: TCPA and FCC Requirements
Check these TCPA and FCC items before your voice agent makes its first production call. The 2024 FCC ruling treats AI-generated voices as artificial, which means you must follow the same rules as prerecorded calls.
Get prior express written consent for all marketing calls and store the proof with timestamps.
Classify AI voices as artificial under the TCPA to ensure you stay within legal bounds for robocalls.
State your identity and the call purpose at the start and tell the user they are talking to an AI.
Provide a clear way for users to opt out during the call and update your do-not-call lists in real time.
Industry-Specific Audit Requirements
Healthcare (HIPAA)
Voice agents in healthcare must treat audio recordings as protected health information and require signed agreements from every vendor in your stack.
Sign a Business Associate Agreement with your LLM provider and infrastructure hosts.
Redact patient names and dates of birth from logs and transcripts to follow the minimum necessary rule.
Store recordings in encrypted buckets with access logs that track every read and write event.
Financial services
If your agent processes payments or discusses account balances, you must follow strict data protection and fair lending laws.
Mask credit card numbers in transcripts and audio streams to meet PCI-DSS requirements.
Follow Regulation E rules for error resolution and unauthorized electronic fund transfers.
Audit your model for bias to ensure your agent treats every loan applicant fairly.
Insurance
Insurance agents must follow a patchwork of state laws and specific rules for handling claims data.
Verify that your agent provides required state disclosures before discussing policy terms.
Keep immutable records of claims conversations to settle disputes and meet state audit rules.
Check that your voice bot identifies itself as an automated system in every interaction.
Government
Building for government agencies means meeting high security bars and ensuring every citizen can use the service.
Host your voice AI on FedRAMP authorized infrastructure to meet federal security standards.
Section 508 accessibility requirements so users with hearing or speech impairments can interact.
Developer Tip: Always check if your LLM provider stores prompts or completions for training, as this can break your HIPAA or PCI compliance overnight.
How Automated Testing Solves the Compliance Problem?
Manual auditing cannot keep up with thousands of live calls. Automation fixes this by running thousands of test paths that check for transcription errors and compliance breaks before they hit production. You can simulate realistic voice interactions, including background noise and user interruptions, to see how your agent holds up under pressure.
How Automated Testing Works
Simulation: Run thousands of edge case calls without paying for production minutes to find failures that spot checks miss.
Audio Verification: Ensure legal disclosures trigger at the right second in the audio file, not just in a text log.
Data Redaction: Scan every API payload and transcript for PII to stop leaks before they reach your storage logs.
Live Monitoring: Track consent rates and rule violations while calls are active to prevent costly legal fines.
Future AGI provides this automation stack in a single platform. It covers simulation-based testing, audio-native evaluation, PII scanning, and production monitoring with built-in compliance reporting. The system uses direct audio evaluation to catch latency spikes and tone shifts that text-only testing misses.
Using Automated Testing for Compliance Validation with Future AGI
9.1 Simulating compliance scenarios at scale
Manual testing can't catch every edge case, so automated compliance tests let you simulate thousands of conversations before your agent ever talks to a real user. Future AGI lets you run simulation-based evaluations that recreate realistic voice interactions including edge cases like user interruptions, background noise, and off-script turns without consuming production call minutes.
Generate test scenarios that trigger opt-out requests at different points in the conversation.
Simulate users asking "Is this a real person?" to verify your AI disclosure fires correctly.
Test consent flow failures like missing checkboxes or expired agreements.
Run regression tests after every model update to catch new compliance breaks.
9.2 Testing disclosure delivery and timing
Your agent must identify itself as AI and announce recording at specific moments, so automated tests should verify both the content and timing of these disclosures. Future AGI provides audio-native evaluation(configuration required) that checks whether disclosures happen at the right conversational moment, not just whether the text appears in a transcript.
Verify AI identification happens within the first 10 seconds of every call.
Check that recording notices play before the user shares sensitive data.
Test disclosure clarity across different voices, accents, and speech rates.
Confirm opt-out instructions are understandable and actionable.
9.3 PII handling verification across conversation paths
Voice agents can leak PII in logs, transcripts, or through third-party integrations, so you need automated scans that check every data flow. Real-time AI speech analytics platforms can monitor conversations for sensitive information and flag potential PII breaches while maintaining compliance with GDPR and SOC 2.
Run automated scans for credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, and health data in transcripts and audio files.
Test that your agent redirects users when they try to share payment info over the phone.
Verify that PII gets redacted from logs before they reach your analytics dashboard.
Check third-party API payloads to ensure no sensitive data leaks to external providers.
9.4 Documenting test results for auditors
Instead of waiting for an auditor to find problems, you use Future AGI to identify and fix them during development.
Check AI disclosures: Use evaluation frameworks to verify that your agent identifies itself as AI within the required timeframe .
Trace opt-out logic: Inspect detailed traces to see exactly where the logic failed when an agent ignored a "stop" request .
Scan for PII leaks: Monitor real-time performance to detect and filter sensitive information before it hits your permanent logs .
Benchmark model updates: Compare different model versions to ensure a new update does not remove existing compliance guardrails .
Monitor production behavior: Track live calls to detect anomalies and verify that your agent remains compliant in the real world .
Future AGI helps you build a reliable history of internal checks . You can see which versions of your agent passed your internal evaluations, giving you the confidence that you are ready for the official auditing process.
Setting Up Continuous Compliance Monitoring
10.1 Real-time compliance dashboards
Future AGI's production monitoring tracks your voice agents as they run, so you can spot compliance issues before they become audit findings.
View live metrics for AI disclosure rates, opt-out request handling, and consent verification across all active agents.
Track PII exposure incidents with drill-down views showing exactly which calls leaked sensitive data.
Monitor model accuracy drops that might cause your agent to skip required disclosures or mishear opt-out requests.
Set up custom compliance metrics that match your industry requirements like HIPAA minimum necessary or TCPA consent timing.
10.2 Automated alerts for compliance violations
Configure alerts that fire when your agent breaks a compliance rule so your team can fix the issue in minutes instead of discovering it during an audit.
Trigger alerts when AI disclosure fails to play in the first 10 seconds of a call.
Get notified immediately if PII appears in unencrypted logs or third-party API calls.
Set thresholds for consent verification failures and route alerts to legal and engineering channels.
Receive daily summaries of compliance violations with severity rankings and affected call counts.
10.3 Audit trail generation for regulatory review
Future AGI automatically generates immutable audit logs that show what your agent said, when it said it, and how users responded.
Export timestamped records of every consent request, disclosure, and opt-out for TCPA audits.
Pull reports filtered by date range, agent version, or compliance category to answer specific auditor questions.
Store audit trails in tamper-proof storage that meets SOC 2 and HIPAA retention requirements.
10.4 Connecting testing to compliance documentation
Link pre-launch test results with production monitoring data so auditors can see your compliance posture from first test to live deployment.
Map test scenarios to specific compliance rules and show pass rates over time.
Connect simulation results with production incidents to prove your testing covers real-world failure modes.
Generate compliance reports that include both automated test data and live call metrics in a single view.
Track how code changes and model updates affect compliance scores across your entire testing and production pipeline.
Conclusion
Auditing your voice AI before launch comes down to a clear checklist: validate consent and disclosures, lock down data handling, and prove that your agent behaves correctly across real-world scenarios. A structured audit framework plus automated testing turns compliance from a one-off task into a repeatable part of your release cycle.
If you want to make this part easier, Future AGI helps you generate synthetic test conversations, benchmark voice agents, and monitor production calls from a single place. You can track accuracy, catch policy breaks, and feed evaluation results back into your agent workflow for continuous improvement.
FAQs